Diamond is a famous mineral, whose name comes from the ancient Greek word “adamas” which means invincible, invincible due to its great hardness as in antiquity all hard stones, which were impossible to process were called adamantas. Diamonds are made of pure carbon and are formed by the transformation of carbon under pressure and heat. Due to its hardness it is used in industrial applications, while its brilliance makes it the most famous and sought after gemstone. Its degree of hardness on the Mohs scale is 10 and its weight is measured in carats (1 carat = 200 millimeters per gram).
The four properties that determine the value of a diamond according to the GIA (Gemological Institute of America) are:
- carats
- clarity
- color
- cut
Carats
It is the unit of weight for a diamond that was first adopted in the United States in 1913 and has since become international. More specifically, one carat equals 0.2 grams. That is, a diamond weighing 5 carats is equivalent to one gram.

Clarity
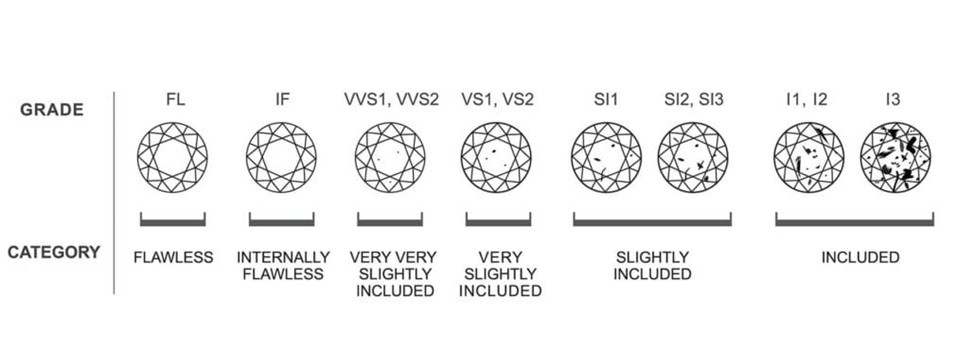
Because of the way they are created in the depths of the earth, diamonds contain foreign bodies, known as inclusions. Diamonds that are free of inclusions are rare and therefore the presence or absence of inclusions affects their price. The world-renowned method for describing the degree of purity of a diamond is that provided by the GIA. According to the GIA-IGI-HRD report there are five basic degrees of purity tested under 10x magnification:
- Internally Flawless (IF): The inclusions of this scale are not visible even with a 10x magnification scale. Diamonds of this category are the rarest and most valuable diamonds.
- Very, Very Slightly (VVS): Inclusions of this scale are quite difficult to detect even on a 10x magnification scale.
- Very Slightly (VS): Inclusions of this scale are quite small in size and sometimes difficult to detect with a 10x magnification scale (VS1) while other times they are easy to detect (VS2).
- Slightly Included (SI): Inclusions of this scale are very small in size and are either easy to detect under 10x magnification (SI2) or easy to detect at 10x magnification but cannot be detected with the naked eye (SI1).
- Imperfect (I): The inclusions of this scale are large in size and quite large in quantity and are visible to the naked eye.
Color
The GIA (Gemological Institute of America), which is the most common color scale, starts with the letter D, which symbolizes the completely colorless diamond and reaches Z, which indicates a diamond with a visible shade of yellow or brown. Intermediate colors indicate how distinct the color of the diamond is.
Diamonds according to their color are divided into:
- Colorless: Diamonds in this class are colorless and are divided into subcategories depending on whether they are transparent (Classes D and E) or almost transparent (Class F).
- Near Colorless: Diamonds in this class are almost transparent (Class G), or white (Class H) or slightly white (Class I and J).
- Slightly Tinted: Traces of color (Categories K, L and M) appear on the diamonds of this category.
- Colorless: Diamonds in this class are colorless and are divided into subcategories depending on whether they are transparent (Classes D and E) or almost transparent (Class F).
- Near Colorless: Diamonds in this class are almost transparent (Class G), or white (Class H) or slightly white (Class I and J).
- Slightly Tinted: Traces of color (Categories K, L and M) appear on the diamonds of this category.

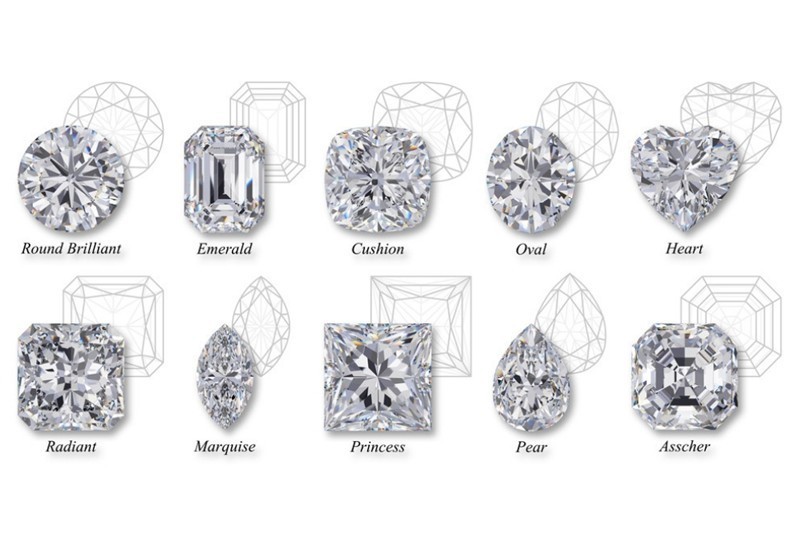
Cut
The cutting (cutting or processing) of the diamond is the most important stage, after which the stone takes its final shape and shows all its beauty. The cutting of the diamond is important because it highlights the brilliance, reflectivity and sparkle of the stone.
There are many different diamond cuts such as Pear, Oval, Heart, Marquise, Moon Drop, Square, Baguette, Round, Brilliant.
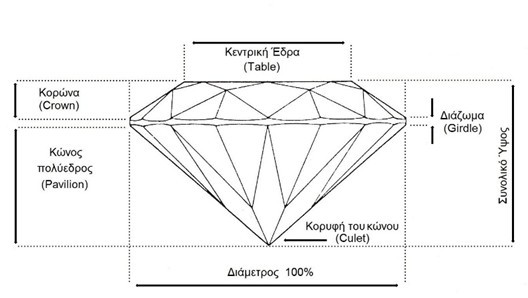
To better understand the cut of a diamond, we need to look at a diamond from the side (profile). As we look at the diamond from the side, the top of the diamond is known as the crown, the middle part of the diamond, that is where the crown and the cone meet is known as the girdle, while the lower part which extends from the diamond cone to the narrow face of the stone is also called the pavilion. The way diamonds are cut greatly influences the way in which light emerges from diamonds. The most popular diamond cut is considered to be the brilliant cut, as it is the one that highlights in the best way the light that passes through the diamond.